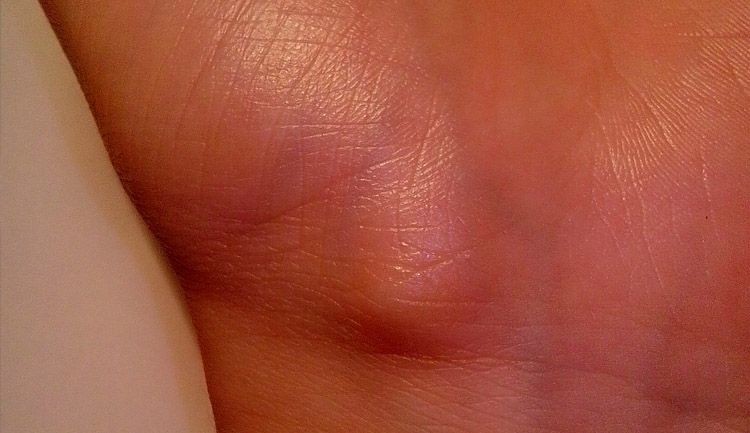
What Causes Ganglion Cysts?
A Ganglion cyst is a swelling on the covering of a tendon, i.e., on the tissue which connects bone to muscle or on top of a joint. It is like a sac of liquid which contains a jellylike fluid called synovial fluid. Ganglion cysts are also known as Synovial cysts, Bible cysts or Bible bumps. A Ganglion cyst may be as small as a pea or may even be close to an inch in diameter.
Ganglion cysts often form over a tendon or joint in the wrists, ankles, fingers, shoulders, elbows, knees or soles of the feet and may feel firm or spongy, depending upon the size of the cyst. Symptoms associated with Ganglion cysts include pain and discomfort along with a tingling sensation, muscle weakness or numbness.
Proneness to develop a Ganglion cyst
Ganglion cysts generally occur in people between the ages of 15 and 40 years of age. Women and gymnasts who repeatedly need to put pressure on their wrists are more prone to develop these cysts. Osteoarthritis patients also have a tendency to develop a Ganglion cyst. An injury to a joint or tendon can also trigger the development of Ganglion cysts.
Cause of Ganglion Cysts
The exact cause of Ganglion cyst is still not known. According to one theory, tissues of the joint break down due to a trauma, resulting in the formation of small cysts which later join to form a larger mass. A flaw in the tendon covering allows the joint tissue to bulge out. A cyst which looks like a small water balloon grows out of the tendon lining or a joint and has a thick viscous fluid inside it. This fluid is similar to the one found in joints or around tendons. As per one explanation, the cause of Ganglion cyst may be understood as the leakage of synovial fluid from the joint to the surroundings.